Flow Separating, and L2 Mirroring and Bridging
Tutorial of SF-TAP cell incubator
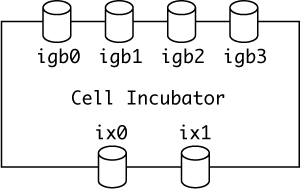
Here, suppose that you have a following FreeBSD box, which has two 10 GbE (ix0 and ix1) and four 1 GbE (igb0, igb1, igb2 and igb3) interfaces.
Flow Based Separating
You can use qb-separator for traffic separating as follows, where -l and -t mean a prefix of “LEFT” and “TAP”, respectively. qb-separator must be executed with root privilege.
# ./qb-separator -l ix0 -t igb0,igb1,igb2,igb3
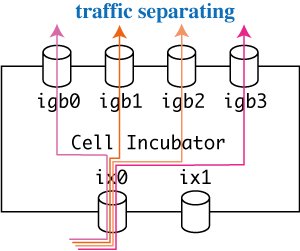
Here, qb-separator captures traffic from ix0, then separates and forwards it to igb[0-3]. Note that it separates traffic by using the hash values of IP addresses and port numbers of captured packets.
Mirroring
You can also use qb-tap for traffic mirroring as follows. qb-tap must be also executed with root privilege.
# ./qb-tap -l ix0 -t igb0,igb1,igb2,igb3
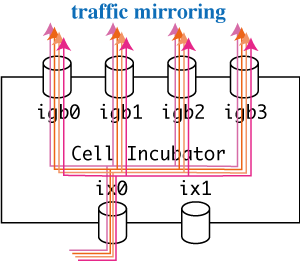
Here, qb-tap forwards all captured traffic from ix0 to igb[0-3].
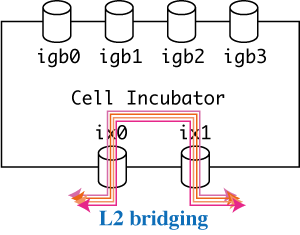
L2 Bridging
You can use qb-separator or qb-tap as a simple software L2 bridge as follows, where -r means “RIGHT”.
# ./qb-separator -l ix0 -r ix1
L2 Bridging + Flow Based Separating
You can use qb-separator as a L2 bridge and a traffic separator as follows.
# ./qb-separator -l ix0 -r ix1 -t igb0,igb1,igb2,igb3

Here, qb-separator separates all traffic from ix0 and ix1, and forwards it to igb[0-3].
L2 Bridging + Mirroring
Similarly, qb-tap can work as an L2 bridge and a traffic mirroring box as follows.
# ./qb-tap -l ix0 -r ix1 -t igb0,igb1,igb2,igb3

Here, all traffic caputured from ix0 and ix1 is forwarded to igb[0-3].